Decoding the P Wave on ECG: What It Really Means!

The atrial depolarization occurring in the heart, is the core process the p wave on the ecg represents, a vital concept for medical professionals. Electrocardiography (ECG), as a diagnostic tool, provides the means to assess this electrical activity. Dr. Willem Einthoven, a pioneer in electrocardiography, established the foundational understanding of waveform interpretation that continues to be the basis for the analysis for cardiac function. An ECG machine, records the electrical signals from the heart. Interpreting these waves ensures that physicians can have a deeper understanding, hence this topic is crucial to their practice and for the benefit of their patients.

Image taken from the YouTube channel Dr. John Campbell , from the video titled P,Q,R,S,T waves in the EKG .
Decoding the P Wave on ECG: What It Really Means!
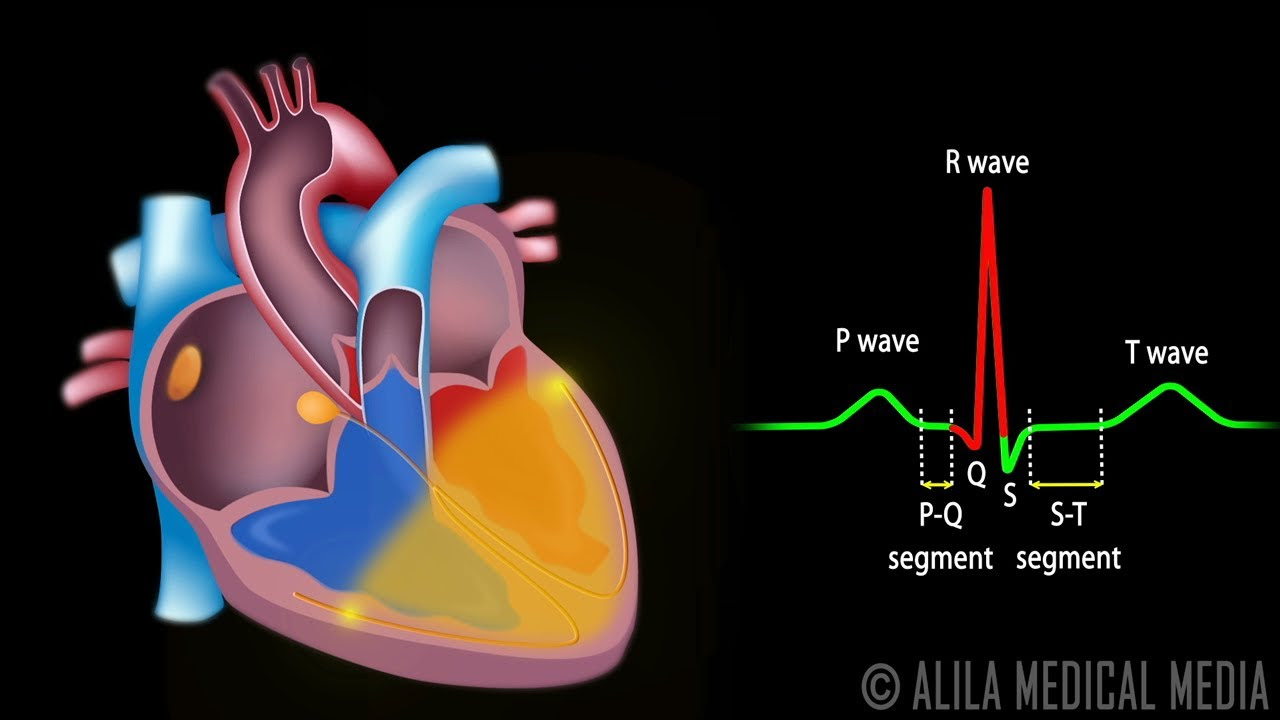
Understanding an electrocardiogram (ECG) can seem daunting, but focusing on individual components, like the P wave, makes it more manageable. The P wave is a crucial part of the ECG reading because the P wave on the ECG represents the electrical activity associated with atrial depolarization. Let's break down what that means and how to interpret it.
What is Atrial Depolarization?
Before we can understand the P wave, we need to understand atrial depolarization.
The Heart's Electrical System in Brief
The heart doesn't beat randomly; it follows a precise electrical pathway. This pathway starts in the sinoatrial (SA) node, often called the heart's natural pacemaker.
- The SA node generates an electrical impulse.
- This impulse spreads through the atria, the upper chambers of the heart.
- This spread of electrical activity is called depolarization. Depolarization causes the atria to contract, pumping blood into the ventricles.
Depolarization Explained
Depolarization essentially means the change in electrical potential across the cell membrane of the heart muscle cells. This change allows the cells to contract. In the atria, depolarization triggers atrial contraction.
The P Wave: Visualizing Atrial Depolarization
The P wave on the ECG is a graphic representation of this atrial depolarization. It shows the electrical activity as the impulse travels through the atria. Therefore, the P wave on the ECG represents the electrical activity of the atria contracting.
P Wave Characteristics
A normal P wave has certain characteristics:
- Shape: Usually smooth and rounded.
- Amplitude (Height): Typically less than 2.5 mm (2.5 small squares) in height.
- Duration (Width): Normally less than 0.12 seconds (3 small squares) in duration.
- Polarity: Usually positive (upright) in leads I, II, and aVF.
Significance of Lead Placement
ECG leads are placed on the body to record the heart's electrical activity from different angles. This is crucial for accurate interpretation. For instance, a P wave might be upright in one lead and inverted (negative) in another lead. This information helps determine the origin and direction of the electrical impulse.
Interpreting Abnormal P Waves
Deviations from the normal P wave characteristics can indicate various heart conditions.
Common P Wave Abnormalities
Here's a table summarizing some common P wave abnormalities and their potential implications:
| P Wave Abnormality | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Absent P Wave | No P wave visible before the QRS complex. | Atrial fibrillation, sinoatrial node dysfunction, or other arrhythmias where atrial depolarization is not occurring in a coordinated fashion. |
| Tall, Peaked P Waves (P Pulmonale) | Amplitude greater than 2.5 mm in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF). | Right atrial enlargement, often seen in patients with pulmonary hypertension, chronic lung disease, or tricuspid valve stenosis. |
| Wide, Notched P Waves (P Mitrale) | Duration greater than 0.12 seconds, often with a "M" or "double hump" appearance. | Left atrial enlargement, often seen in patients with mitral valve stenosis or regurgitation, hypertension, or left ventricular hypertrophy. |
| Inverted P Waves | P waves that are negative in leads where they are normally positive (e.g., lead I, II, aVF). | Ectopic atrial rhythms (electrical impulse originating from a location other than the SA node), retrograde atrial depolarization (impulse traveling backward from the AV node to the atria), or lead placement error. |
| Variable P Wave Morphology | P waves that change shape and size throughout the ECG tracing. | Wandering atrial pacemaker or multifocal atrial tachycardia, where the electrical impulse originates from different locations within the atria. |
The Importance of Clinical Context
It's crucial to remember that ECG findings, including P wave abnormalities, should always be interpreted in the context of the patient's clinical history, symptoms, and other diagnostic tests. An abnormal P wave on an ECG does not automatically equal a diagnosis; it is one piece of the puzzle.

Video: Decoding the P Wave on ECG: What It Really Means!
Frequently Asked Questions: Understanding the P Wave on ECG
Here are some common questions about interpreting the P wave on an ECG to help you better understand atrial activity and heart function.
What does the P wave on the ECG represent?
The p wave on the ecg represents atrial depolarization, or the electrical activation of the atria. This is when the atria are contracting to pump blood into the ventricles. A normal P wave indicates proper atrial function.
What can an abnormal P wave tell me?
Abnormal P waves can indicate various atrial abnormalities. For example, enlarged atria, atrial fibrillation or flutter, or ectopic atrial rhythms. The specific shape and size of the P wave, as well as its relationship to other ECG components, are key to diagnosis.
How does the P wave relate to other parts of the ECG complex?
The P wave precedes the QRS complex, which represents ventricular depolarization. The PR interval, the time between the start of the P wave and the start of the QRS complex, reflects the time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
What should I do if my ECG shows an abnormal P wave?
An abnormal P wave requires further evaluation by a healthcare professional. They will consider your symptoms, medical history, and other ECG findings to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment or management strategies.